Definition and differences between complete fractures, incomplete fractures
A fracture is defined by the discontinuity or breakage of bones of the human body.
There are:
Closed fractures
This type of fracture is no wound and therefore no risk of infection.
Open fractures
This type of fracture is followed by a wound and risk of infection.
Complete fractures incomplete fractures
Incomplete fractures are fairly typical of the child because the bone can break partially while respecting the continuity of the periosteum that surrounds it.
All the bones may be involved at all stages of life.![]()
Risks and health issues fractures
If all the bones can be achieved, some fractures are more common than others: wrist, femoral neck (elderly), ankle, leg and upper limbs.
Fracture risk factors are now identified: personal history of fracture fragility, age> 60 years, corticosteroids, history of fracture of the proximal femur in a first-degree relative, body mass index (BMI = weight / height squared) <19, early menopause (before age 40), smoking, alcohol abuse, decreased visual acuity, neuromuscular and orthopedic disorders.
Causes and mechanisms of fractures
The periosteum covers the long bones, flat and allows their growth. In case of incomplete fracture, periosteum is respected despite a broken bone underneath.
Fractures are directly related to bone mass. Its reduction or deterioration of bone tissue results in an increased risk of fracture. Bone strength can be assessed by measuring bone mineral density (BMD) by densitometry. This measure is useful only for those at risk of osteoporosis (bone loss).
How manifests a fracture?
Any trauma can cause a fracture whose main symptoms are a cracking, pain and swelling of the fractured region.
Distortion may be visible or not according to the angulation of the fracture: in incomplete fractures, angulation and deformation are not marked.
Pain causes functional impairment, with inability example to set foot on the ground or to use the affected limb.
With what would it be confused fractures?
It should not be confused sprain or strain that affect joints and ligaments and fractures involving bones. A sprain can, however, be accompanied by avulsion fracture.
At the level of a member, a sharp pain with impotence can be caused by a muscle tear without fracture; only radiography make the difference.
Will it possible prevention of fracture?
The best prevention is still a good physical preparation, proper warm-up and a conservative sport.
Wearing appropriate clothing (knee, shin guards, helmet ...) avoids direct trauma.
The fight against risk factors is also recommended to prevent fractures. The diet should be balanced to avoid excess weight but also fight against deficiencies (lack of calcium and / or vitamin D). Tobacco and alcohol are two enemies of the bones and weaning is recommended.
If demineralization proven to bone densitometry (osteoporosis), hormone replacement therapy is offered in postmenopausal women (in the absence of cons-indication) and drugs fighting against bone destruction are available to all.
Fractures: when to consult?
Any persistent pain, swelling or deformity after trauma requires a medical consultation and possibly a radiograph.
Unnoticed or ignored, a fracture can worsen and cause chronic pain, osteoarthritis and / or deformation.
What does the doctor faces a divide?
The doctor will clarify the antecedents and fracture risk factors (see above), the mechanism of trauma and violence. He then studied active and passive motility of the member concerned asking you to move spontaneously. Finally, palpation of bony prominences can highlight deformation or painful point.
Only an x-ray will help confirm the diagnosis. In children, radiographs are sometimes difficult to interpret.
The curvature traumatic results in exaggerated bone curvature without obvious feature of fracture.
The green wood has a fracture line on one side of the bone fracture, but the other side is respected; finally, the lump of butter fracture corresponds more to a slowdown in the bone.
Fracture treatment is based on the quiescence of the bone and joints, pain medication and immobilization (plaster, resin ...).
Depending on the case and the deformation, surgery can be necessary to refocus or secured fragments.
How to prepare for my next visit?
We must not neglect pain following trauma and view. In case of cast immobilization, any pain should be reported to the doctor to check the cast is not too tight and does not interfere with traffic.
If anticoagulant therapy is prescribed (spots) must be followed carefully to prevent phlebitis.
A fracture is defined by the discontinuity or breakage of bones of the human body.
There are:
Closed fractures
This type of fracture is no wound and therefore no risk of infection.
Open fractures
This type of fracture is followed by a wound and risk of infection.
Complete fractures incomplete fractures
Incomplete fractures are fairly typical of the child because the bone can break partially while respecting the continuity of the periosteum that surrounds it.
All the bones may be involved at all stages of life.
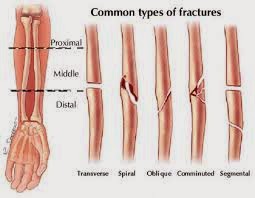
Risks and health issues fractures
If all the bones can be achieved, some fractures are more common than others: wrist, femoral neck (elderly), ankle, leg and upper limbs.
Fracture risk factors are now identified: personal history of fracture fragility, age> 60 years, corticosteroids, history of fracture of the proximal femur in a first-degree relative, body mass index (BMI = weight / height squared) <19, early menopause (before age 40), smoking, alcohol abuse, decreased visual acuity, neuromuscular and orthopedic disorders.
Causes and mechanisms of fractures
The periosteum covers the long bones, flat and allows their growth. In case of incomplete fracture, periosteum is respected despite a broken bone underneath.
Fractures are directly related to bone mass. Its reduction or deterioration of bone tissue results in an increased risk of fracture. Bone strength can be assessed by measuring bone mineral density (BMD) by densitometry. This measure is useful only for those at risk of osteoporosis (bone loss).
How manifests a fracture?
Any trauma can cause a fracture whose main symptoms are a cracking, pain and swelling of the fractured region.
Distortion may be visible or not according to the angulation of the fracture: in incomplete fractures, angulation and deformation are not marked.
Pain causes functional impairment, with inability example to set foot on the ground or to use the affected limb.
With what would it be confused fractures?
It should not be confused sprain or strain that affect joints and ligaments and fractures involving bones. A sprain can, however, be accompanied by avulsion fracture.
At the level of a member, a sharp pain with impotence can be caused by a muscle tear without fracture; only radiography make the difference.
Will it possible prevention of fracture?
The best prevention is still a good physical preparation, proper warm-up and a conservative sport.
Wearing appropriate clothing (knee, shin guards, helmet ...) avoids direct trauma.
The fight against risk factors is also recommended to prevent fractures. The diet should be balanced to avoid excess weight but also fight against deficiencies (lack of calcium and / or vitamin D). Tobacco and alcohol are two enemies of the bones and weaning is recommended.
If demineralization proven to bone densitometry (osteoporosis), hormone replacement therapy is offered in postmenopausal women (in the absence of cons-indication) and drugs fighting against bone destruction are available to all.
Fractures: when to consult?
Any persistent pain, swelling or deformity after trauma requires a medical consultation and possibly a radiograph.
Unnoticed or ignored, a fracture can worsen and cause chronic pain, osteoarthritis and / or deformation.
What does the doctor faces a divide?
The doctor will clarify the antecedents and fracture risk factors (see above), the mechanism of trauma and violence. He then studied active and passive motility of the member concerned asking you to move spontaneously. Finally, palpation of bony prominences can highlight deformation or painful point.
Only an x-ray will help confirm the diagnosis. In children, radiographs are sometimes difficult to interpret.
The curvature traumatic results in exaggerated bone curvature without obvious feature of fracture.
The green wood has a fracture line on one side of the bone fracture, but the other side is respected; finally, the lump of butter fracture corresponds more to a slowdown in the bone.
Fracture treatment is based on the quiescence of the bone and joints, pain medication and immobilization (plaster, resin ...).
Depending on the case and the deformation, surgery can be necessary to refocus or secured fragments.
How to prepare for my next visit?
We must not neglect pain following trauma and view. In case of cast immobilization, any pain should be reported to the doctor to check the cast is not too tight and does not interfere with traffic.
If anticoagulant therapy is prescribed (spots) must be followed carefully to prevent phlebitis.